Chronic prostatitis is an inflammatory process of the male prostate with a long course (more than six months).
Usually this pathology is the result of an infection process.
The treatment of chronic prostatitis aims to eliminate the pathogen of the infection.
The lack of such treatments can lead to various dysfunctions and complications, up to male infertility.

Causes of chronic prostatitis Various pathogens (pathogens) microorganisms lead to the development of inflammatory response and its long process.
There are two major types of pathogens in chronic prostatitis:
- Non-specific bacterial infection– Pathogenic microorganisms that can cause inflammation in different organs, including Streptococcus, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella, Proteus, and Staphylococcus.
- Specific infection.Pathogenic microorganisms are only parasitic in the structure of the male genitourinary tract (Chlamydia, Ureaplasma, Trichomonas).
Understanding the reasons for the development of chronic inflammation of the prostate is necessary for the subsequent selection of reasonable symptomatic treatment.
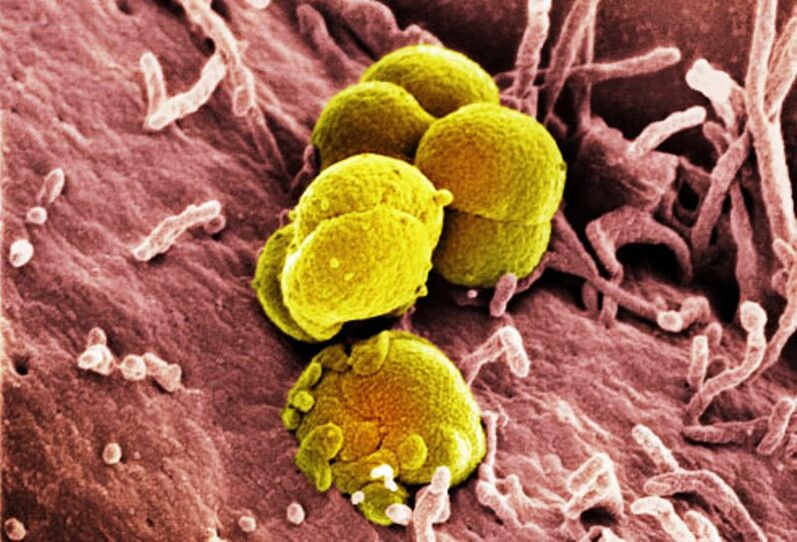
Its purpose is to destroy pathogens.
Other factors can also contribute to the development of chronic prostatitis.
The stagnation of blood in the small pelvis leads to insufficient oxygen exchange in the organs and tissues.
This will affect their regeneration and resistance to infection.
The general decline of the body's protective function will trigger the development of inflammation.
Lack of physical exercise will adversely affect human health and lead to a decline in human defenses.
The factors leading to the development of chronic prostatitis include the patient's intimate life problems.
This is the interruption of sexual intercourse without ejaculation, irregular sex life, long-term abstinence.
The consequences of trauma usually affect the condition of the genitals.
Overwork, stress, and other reasons can cause prostate problems.
Heavy drinking and smoking can cause disruption of the male reproductive system.
Classification of prostatitis
There are three types of diseases:
- bacterial;
- Non-bacterial
- Prostate pain.
The first type is characterized by the detection of microorganisms in the emissions.
In order to treat this species, antibacterial drugs are needed.
A non-bacterial condition is a condition where there are no bacteria in the glandular secretions.
Prostatic pain is a characteristic complaint of prostatitis, but there is no abnormal process in the analysis of prostate secretion.
Treatment of chronic prostatitis with pathology
Patients with prostate problems usually have other problems.
These may be cardiovascular disease, respiratory system and digestive system disease.
For these patients, the treatment plan will be different.
In order to properly adjust the treatment, a proper diagnosis must be made.
Consultation on such cases may involve narrow-minded experts.
Treatment of adolescent chronic prostatitis
By the age of 30, the infectious agent is usually the cause of prostatitis.
This is related to the lifestyle of young people.
Failure to treat bacterial and viral infections can have an impact.
Promiscuity, neglect of hygiene, and sedentary lifestyle play a role.
Patients rarely see a doctor at the first signs of illness.
The disease progresses and becomes chronic.
It is worth paying attention to these issues and minimizing the risk of their impact.
As a precaution, it is recommended to conduct an inspection every year.
Obesity treatment
The problem of extra weight can negatively affect a man's internal organs.
Elevated levels of cholesterol, blood pressure, and glucose can cause metabolic disorders.
Lack of continuous physical activity can cause blood stagnation in the pelvic organs and lead to the development of inflammation.
Timely weight loss and prevention can have a beneficial effect on overall health.